
Why? As a scientist you want to control the environment - keeping the protein you are interested in at a non-denaturing pH, you want to keep it from being cleaved by enzymes that will be released in this process so general inhibitors will be important, etc. This is always done in the presence of a buffer and inhibitors. Once you have gathered the material containing the protein you want to study it is necessary to generate a crude extract - for proteins from muscle that would mean grinding it up, for an intercellular protein that would mean breaking the cells open, etc. metabolic enzymes) so they could be isolated in large abundance from other sources, such as yeast or bovine. Also many proteins are common to a large number of species (e.g. Historically the abundance and ease of isolation dictated which proteins were first studied (e.g. To being any sort of purification procedure you need to obtain the material from which you plan the isolate the material. These will be discussed in more detail later. Immunological (using a antibody that can recognize the protein of interest) Spectroscopic (using Bradford reagent or a chromagenic substrate) Assays come in many different forms and depends in a large part on the type of protein you are trying to purify (i.e. To begin any sort of purification it is important that an assay be available to identify where the protein of interest is after the fractionation. A Da is the same as an atomic mass unit which is approximately the mass of a nucleon and is equivalent to 1 g/mol. MW is usually expressed in daltons (Da) or kilodaltons (kDa). For example the molecular weight (MW) of a protein is just the summation of the masses of the individual AAs composing the protein. These properties of a protein are derived from the AA properties composing the protein. Protein purification methods use fraction techniques which are in a large part based on: These methods, or derivatives of the methods, are used in the clinical labs to identify abnormal samples. It is through protein purification methods that we have been able to study and understand proteins in detail. At high pH, the protein is negatively charged and is strongly attracted to a positively charged surface.Foundations of Clinical Sciences Protein Purification Methods At the pI, the protein has net zero charge and experiences weaker attraction to the surface. How does pH affect net charge of protein?Īt low pH, the proteins are positively charged, and are strongly attracted to a negatively charged surface. The lactic acid production lowers the the pH of milk to the IEP of casein. The lactic acid bacillus produces lactic acid as the major metabolic end-product of carbohydrate fermentation. What caused the milk proteins to reach its isoelectric point? Which amino acid has the highest pI value? Amino acid Minimum solubility values for any salt are at a pH of 5.0 in this condition, the electrostatic forces are the lowest and less water interacts with the protein molecules, which causes the increase of proteinprotein interactions. Protein solubility is lower in acidic pH than in alkaline pH. Read More: Can HIV positive work in Japan? How does pH affect solubility of protein? … At a pH below their pI, proteins carry a net positive charge at pH values above their pI they have a net negative charge. Many molecules are zwitterions, containing both positive and negative charges. The isoelectric point is the pH at which a molecule or surface carries no net electrical charge. What is isoelectric point explain with example? In order to determine the isoelectric point a given protein, we must follow a general rule that consists of two steps (1) Estimate the pH value at which the protein will have a net charge of zero (2) Determine the pKa value right above and right below the estimated pH and find their average.
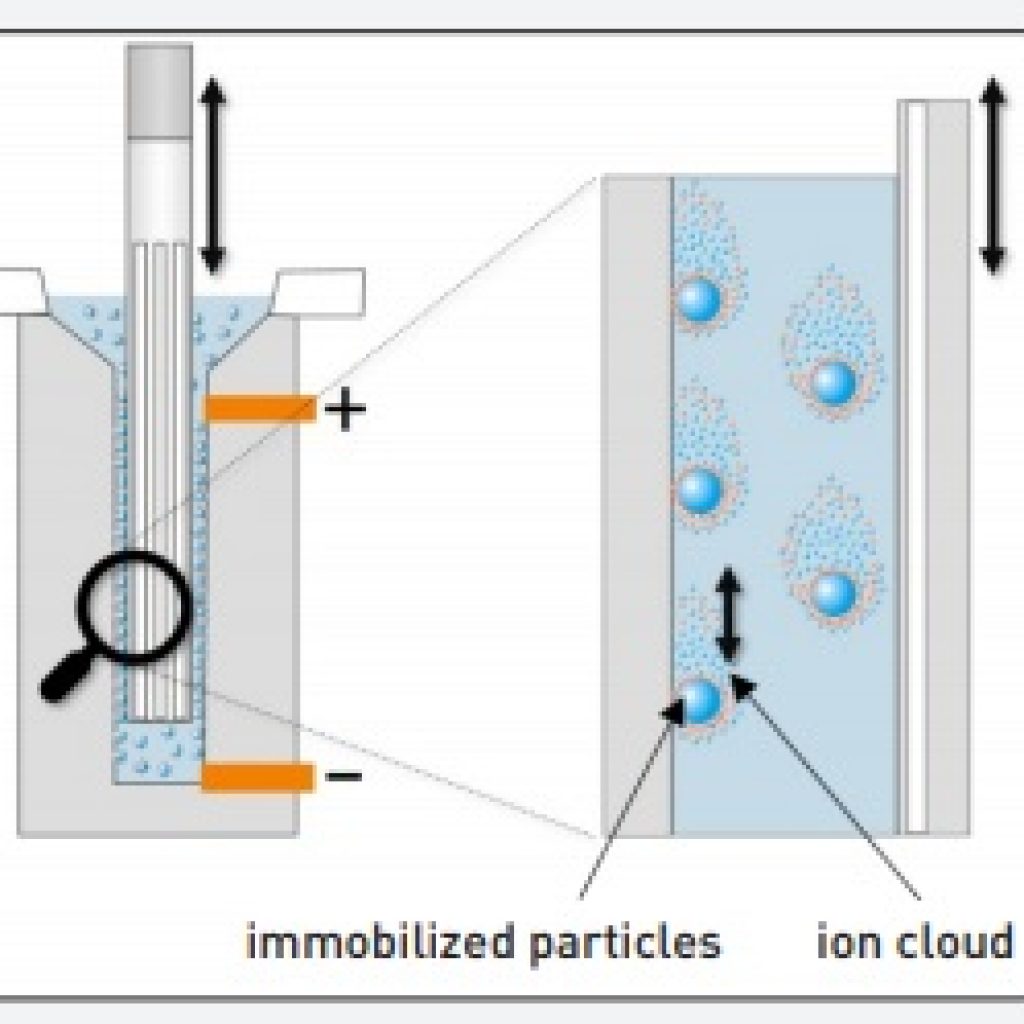
How do you find the isoelectric point of a protein? … When this pH gradient is in development, protein molecules simultaneously migrate in the solution until these molecules reach their protein isoelectric point. Above the isoelectric point, a protein carries a net negative chargebelow it, a net positive charge. How does isoelectric point affect proteins?Īt the isoelectric point, a protein has no net charge. … The pI value can be used to indicate the global basic or acidic character of a zwitterionic molecule, and compounds with pI > 7 can be considered basic, and those with pI < 7 can be considered acidic.
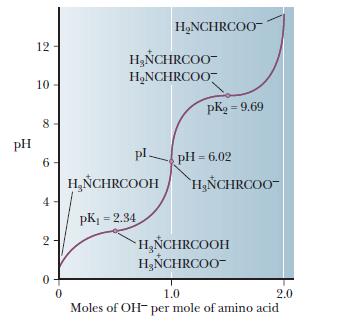
The isoelectric point (pI) is the pH value at which the molecule carries no electrical charge.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
